38 Irrawaddy Road #08-51, Mount Elizabeth Novena Specialist Centre, Singapore 329563

Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Early-stage coronary artery disease often goes undetected by standard electrocardiograms (ECGs) or non-invasive ECG stress tests in Singapore. This is where CT coronary angiograms help in identifying heart artery blockages at their earliest stages, enabling early intervention to slow the progression of the disease and prevent severe blockages or heart attacks.
Evaluating the Extent of Artery Narrowing
CT coronary angiograms are used to measure the extent of narrowing in the coronary arteries caused by fatty and calcified deposits. This evaluation helps the doctor determine the most appropriate treatment approach, which may include lifestyle changes, medication, or medical procedures such as stenting or bypass surgery.
Assessing the Function of Stents and Bypass Grafts
Over time, the risk of blockages developing in coronary stents or bypass grafts can increase, especially if risk factors like diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol are not well managed. A CT coronary angiogram can help evaluate your condition and may reduce the need for more invasive procedures, such as cardiac catheterisation.
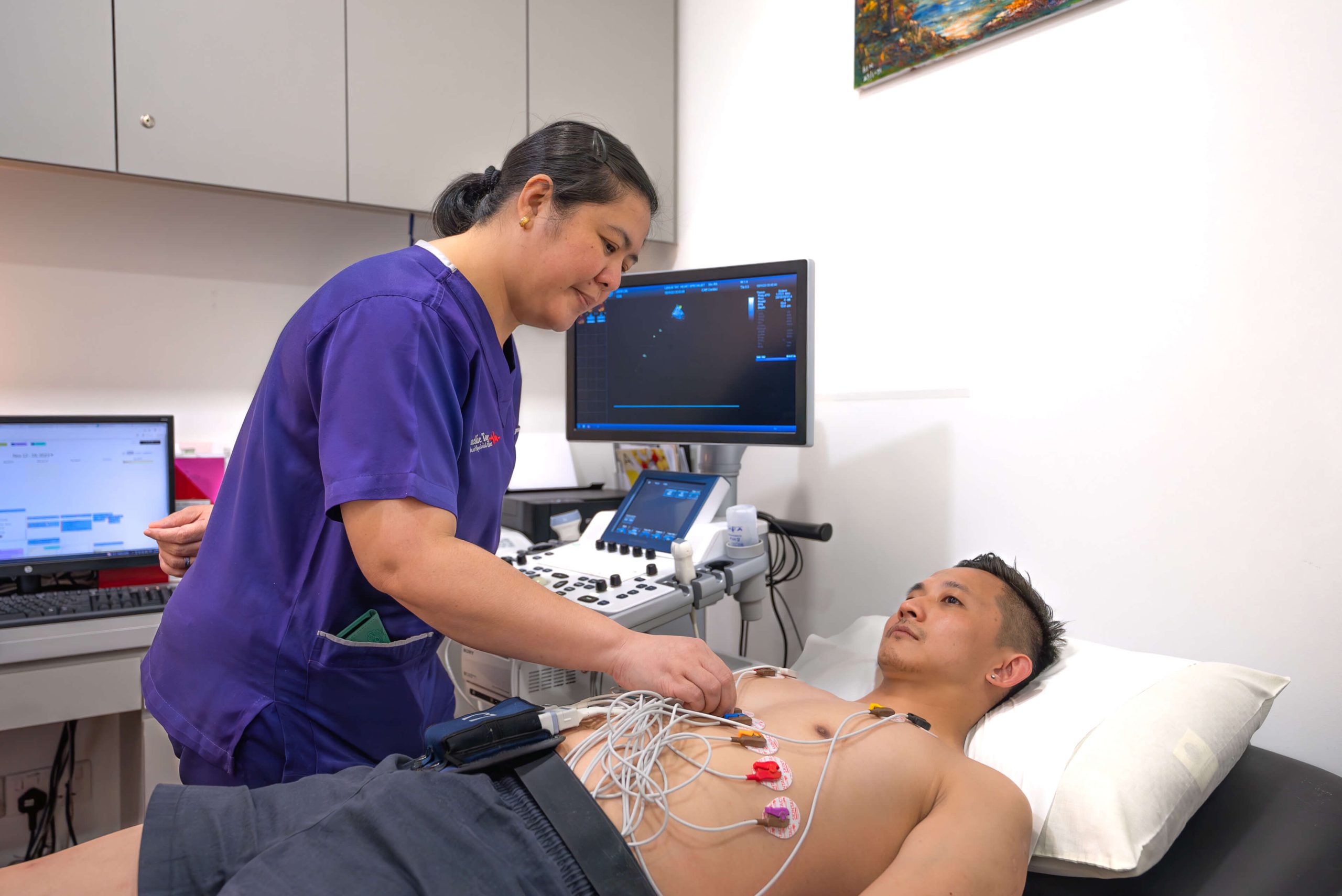
Treating Complex CAD
For patients with complex and difficult-to-treat coronary artery blockages, a CT coronary angiogram can help enhance the success of procedures like stenting. By providing clear, detailed images of the coronary arteries, it allows doctors to better assess the location, severity, and nature of the blockages. This information is crucial for planning interventions with greater precision, improving the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Identifying Coronary Artery Anomalies
In addition to diagnosing CAD, CT coronary angiograms are also effective in detecting coronary artery anomalies, including congenital defects or unusual artery origins. Early identification of these conditions is vital for developing appropriate treatment plans and reducing the risk of sudden cardiac arrest or other serious heart issues.
How it is Performed:
CT Coronary Angiogram, short for Computed Tomography Coronary Angiography, is a diagnostic procedure utilised to visualise blood vessels in various parts of the body. During the procedure, the patient lies down on the CT scan bed and a small amount of contrast dye is injected through an IV cannula in the hand. The machine captures a series of cross-sectional images within a few seconds. These images are then processed by a computer to create detailed, three-dimensional pictures of the blood vessels. It is sometimes performed as part of a comprehensive heart screening to assess for abnormalities or blockages in the vascular system.
